Households and businesses are finding it increasingly necessary to be online to support their day-to-day operations, as well as adding new technology to enhance services. If you’re experiencing poor Wi-Fi, it’s important to address it quickly since it can impact productivity and operations.
When experiencing slow speeds or unreliable connection, in the first instance, talk to your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Your service provider can give you the best advice based on your situation and will be able to identify if poor service is due to equipment or service subscription that does not fit your needs. However, you can use the below as a guide to help troubleshoot and improve your WI-FI:
Diagnose the Problem
- Check Speed: Use tools like Speedtest.net to measure upload/download speeds.
- Identify Dead Zones: Walk around the space with a device to see where the signal drops.
Basic Fixes
- Restart Router/Modem: A simple reboot can often resolve temporary issues.
- Update Firmware: Ensure your router’s firmware is up to date.
Optimise Your Setup
- Router Placement: Place it centrally and elevated, away from walls or metal objects.
- Use Ethernet: For stationary devices (like POS systems, back office or desktops), wired connections are faster and more reliable.
Upgrade Your Equipment
- Upgrade your ISP router: Check if you have the latest model from your service provider.
- Get a Business-Grade Router: These offer better performance.
- Add Access Points or Mesh Wi-Fi: These extend coverage across larger spaces.
- Use a Wi-Fi Extender: For small dead zones, this can be a quick fix.
Consider a Professional Assessment
- IT Consultant or Network Specialist: They can perform a site survey and recommend tailored solutions.
- Speak with your service provider: They will test your current service and assess your needs to offer more appropriate package.
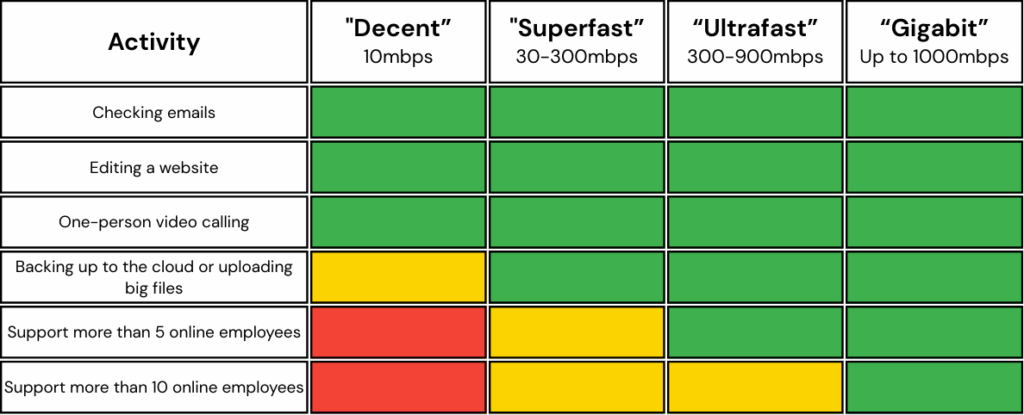
What broadband speeds do I need?
For any home or business, internet connectivity can be essential. With fast, reliable broadband, you can:
- Upload and download files.
- Share bandwidth with multiple users.
- Stream high-quality video
- Communicate with family, friends, customers, clients or visitors.
The table below represents the typical speeds required for common online activities. These can help you decide which speed best suits your needs.
Full fibre or fibre to the cabinet?
What is the difference? The difference between Full Fibre (also known as FTTP – Fibre to the Premises) and Fibre to the Cabinet (FTTC) lies in how far the fibre optic cables go in delivering internet to your property:
Fibre to the cabinet (FTTC) |
Full fibre (FTTP or FTTH) |
| Speeds: Typically up to 80 Mbps download, but can be lower depending on distance from the cabinet. | Speeds: Can reach 1 Gbps or more |
| Fibre runs to a cabinet, usually within a few hundred metres of your home or business. | Fibre runs all the way to your premises, with no copper involved. |
| From the cabinet to your premises, it uses traditional copper telephone lines | Offers much faster and more reliable internet. |
| Reliability: More prone to signal degradation and slower speeds during peak times due to copper | Reliability: Less interference, better for streaming, video calls, cloud services, and multiple users |
| Availability: Widely available across the UK. | Availability: Still rolling out across the UK, but expanding rapidly |
Improving Wi-Fi connection
Firstly, your Wi-Fi connection will only be as good as your broadband service so once you have a service that meets your needs there are things you can do to improve your Wi-Fi.
Where is your router?
Where you place your router can play a big part in how the signal transmits around your property. Wi-Fi signals weaken as they pass through objects and the strength can be affected by materials such as metal, glass, stone, and water. Electrical items can also affect Wi-Fi signal such as a microwave, TV, audio equipment, or cordless phones.
The router’s position in the building is also key. The signal is transmitted all around the router so where practical it should be placed central to the property away from electricals, fish tanks, radiators, and thick stone walls. Ideally, it would be placed on a shelf or side table and if possible, away from the ground. If the router comes with an ariel or two, they should be angled in opposite directions for best coverage.
.
Upgrade your router
Periodically providers upgrade their equipment and often send out a new router to customers. If you haven’t had an upgrade in a few years, then contact your provider to make sure you have the latest model they’re currently providing.
Another option is to purchase an upgraded router not issued by your provider, however, be aware that your broadband provider may not be able to assist if you have connection problems.
Access point network
An access point network is a system where one or more wireless access points are connected to a wired network—typically through Ethernet cables—to extend Wi-Fi coverage across a larger area. Each access point acts as a transmitter and receiver of wireless signals, allowing devices to connect to the internet or local network without needing a direct wired connection. This setup is especially useful in environments such as offices, schools, or large homes where a single router cannot provide sufficient wireless coverage.
Mesh network
Mesh networks connect to your router and can be purchased as an extra onto your contract in packs to fit your needs. These provide their own Wi-Fi network which can improve Wi-Fi coverage without losing performance from your broadband connection. Mesh Wi-Fi systems always come with at least a pair of hubs however you can add extra hubs if you have a larger building or to meet your demand. The system plugs into your existing router for an instant Wi-Fi upgrade.
Connected devices
The number of devices you have connected can affect your Wi-Fi speed as multiple devices share the bandwidth from the same signal. Disconnecting devices that are idle or not needed can improve the data rate and speed of the devices you are using.
Wi-Fi boosters
These can be purchased and placed in areas of the building where the signal is weak to extend coverage. They act in a similar way to a mesh however unlike mesh they can affect your connection speeds.
Powerline adaptor
These use the building’s electrical circuits to transfer the signal from your router to another room. They come in pairs with one plugging into a power socket and connecting directly to your router via ethernet cable, and the other plugging into the room where you are using your device.
Alternative broadband technologies
If you’re experiencing low speeds and fibre-based broadband isn’t available to you currently, there are other ways to connect to broadband. Below are some of the options you may want to consider. You may need to try and see which one works best for your location as the service can vary depending on a number of things including distance from masts, obstructions and aerial location.
4G broadband
4G broadband uses 4G rather than a fixed line (such as a phone line or fibre optic cable) to deliver internet access. A conventional broadband service is wired all the way to your router, whereas 4G broadband is wireless in the same way as getting mobile data on your phone is wireless.
A broadband router can be installed to connect your property to broadband via a 4G mobile network. It doesn’t mean using a mobile phone, and you don’t need cables or a phone line. An external antenna can be attached to the side of your property in areas where a 4G signal might not be strong indoors.
5G broadband
5G broadband is the next step on from 4G broadband. It is connected in the same way as 4G broadband, but it uses the latest 5G technology giving you faster download and upload speeds.
Satellite broadband
Satellite broadband is a satellite internet service that is transmitted using a wireless connection via a satellite dish, similar to those used for satellite TV. A satellite transfers data to and from a dish attached to your property to bring you broadband. Unlike fixed wireless broadband where the radio communication is made with ground-based masts, satellite broadband communicates to a satellite that is orbiting the earth.

